Self-insured health insurance plans are becoming an increasingly popular option for individuals and businesses seeking more control over healthcare costs. Unlike traditional health insurance, where a third-party insurer takes on the financial risk of medical expenses, self-insured plans allow individuals or employers to manage their own healthcare costs. This model can offer significant benefits, but it also comes with its own set of challenges.
In this blog, we’ll explore what self-insured health insurance plans are, how they work, the advantages and disadvantages, and who should consider this option. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a better understanding of how self-insured plans might be a viable solution for managing healthcare expenses.
What Is a Self-Insured Health Insurance Plan?

A self-insured health insurance plan is an arrangement where the individual or employer assumes the responsibility for healthcare expenses instead of relying on an insurance provider. Instead of paying premiums to an insurer, self-insured individuals or businesses allocate funds to an account that covers medical costs as they arise.
In essence, the individual or employer acts as the insurer, directly paying for medical claims, such as doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescriptions. These plans are often structured through Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or similar accounts, where contributions are made over time to build a healthcare fund.
Unlike fully insured health plans, which involve paying a fixed premium to an insurer who assumes the risk of healthcare costs, self-insured plans carry more financial risk. Individuals or employers may face unpredictable medical expenses, but they can also benefit from lower overall costs by avoiding insurance company premiums.
Self-insured health plans can be a good fit for those with predictable healthcare needs or a higher tolerance for financial risk. However, they may not be ideal for those with unpredictable or high healthcare expenses.
How Do Self-Insured Health Plans Work?

Self-insured health plans work by transferring the responsibility of covering healthcare expenses from the insurer to the individual or employer. Here’s how they operate:
1. Funding the Plan
Rather than paying regular premiums to an insurance company, individuals or businesses contribute funds to an account designed to cover healthcare expenses as they occur.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): Many self-insured plans are linked to HSAs, which allow individuals to set aside pre-tax money to cover medical expenses. These funds grow tax-free and can be used to pay for a variety of healthcare costs.
- Employer-Sponsored Accounts: For businesses, they may establish internal accounts or trust funds to cover employees’ medical expenses, rather than purchasing traditional insurance policies.
2. Managing Risk
Since the individual or employer takes on the financial responsibility, risk management becomes crucial. Self-insured plans often include:
- Stop-Loss Insurance: This type of insurance helps protect against unexpectedly high healthcare costs. It kicks in when medical claims exceed a certain threshold, offering financial protection against catastrophic losses.
- Third-Party Administrators (TPAs): Many self-insured employers work with TPAs to manage the plan, including claims processing, network management, and other administrative tasks. This allows employers to focus on running their business, while ensuring efficient management of the healthcare plan.
3. Flexibility in Coverage
One of the major advantages of self-insured plans is the flexibility they provide. Unlike fully insured plans, where coverage is pre-determined, self-insured plans allow the individual or business to:
- Choose Covered Services: You can decide which medical services to cover, rather than relying on an insurance company’s preset plan.
- Adjust the Plan: If your health needs change, you can adjust the plan as necessary to accommodate any shifts in coverage.
Advantages of Self-Insured Health Insurance Plans
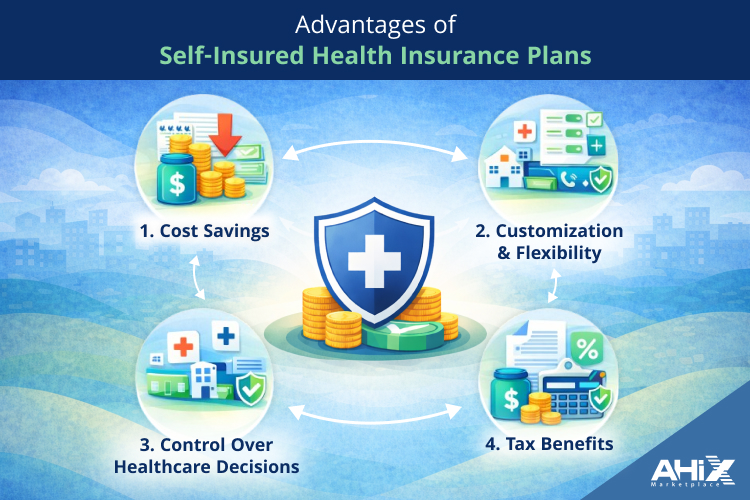
Self-insured health plans offer several compelling benefits, making them an attractive option for individuals and businesses. Here’s a breakdown of the key advantages:
1. Cost Savings
A primary reason for opting for self-insured health plans is the potential for cost savings:
- Lower Premiums: Without the overhead costs associated with traditional insurance companies, self-insured plans often have lower premiums. This is especially beneficial for small businesses or self-employed individuals.
- No Profit Margin: Traditional insurers add a profit margin to premiums. With self-insured plans, you’re only paying for the actual medical costs, not for the profit margin of an insurer.
2. Customization and Flexibility
Self-insured health plans are highly customizable, allowing individuals or businesses to tailor the plan to meet specific healthcare needs:
- Choose Covered Services: Unlike fully insured plans, which offer limited coverage options, self-insured plans allow you to choose which services to cover.
- Adjust Coverage as Needed: As healthcare needs change, the plan can be modified to meet evolving requirements. Whether it’s adding new treatments or changing coverage, the flexibility is a significant benefit.
3. Control Over Healthcare Decisions
With a self-insured plan, you gain more control over healthcare decisions:
- Direct Access to Healthcare Providers: Fewer intermediaries mean more direct relationships with healthcare providers, which can lead to better care and personalized treatment.
- Better Healthcare Management: The freedom to choose treatments and providers can result in more tailored healthcare decisions, benefiting overall health management.
4. Tax Benefits
Self-insured health plans, particularly those linked to HSAs, offer several tax benefits:
- Tax-Free Contributions: Contributions to an HSA are tax-free, which can reduce the overall tax burden for individuals or businesses.
- Lower Employer Costs: For businesses, self-insuring can often lead to lower costs in the long run due to reduced premiums and potential tax incentives.
Risks and Disadvantages of Self-Insured Health Insurance Plans

While self-insured health plans provide several benefits, there are certain risks and disadvantages that should be carefully considered:
1. High Initial Costs
Self-insured health plans require a significant upfront investment:
- Upfront Funding: Individuals or businesses must set aside a large sum of money to fund the plan before any claims arise, which could be a financial strain, especially for smaller businesses.
- Cash Flow Issues: Businesses may experience cash flow challenges as they allocate funds to the health plan, which could divert resources from other operational needs.
2. Unpredictability of Medical Costs
The unpredictability of medical expenses is one of the key risks:
- Large Unexpected Claims: Major health events can result in high medical costs that were not anticipated, leaving individuals or businesses vulnerable without sufficient funding.
- Limited Stop-Loss Protection: While stop-loss insurance provides some protection, there’s still a risk that medical expenses may exceed coverage limits.
3. Limited Network of Providers
Some self-insured health plans may have a limited network of healthcare providers, particularly when managed by third-party administrators:
- Access to Care: The plan may not provide access to the full range of doctors, hospitals, or specialists available through traditional insurance.
- Restrictions on Care: Some self-insured plans may impose restrictions on certain types of care, limiting the options available to plan participants.
4. Regulatory Complexity
Self-insured health plans are subject to complex regulations that vary by state and industry:
- Legal Requirements: Employers and individuals must stay updated on changing laws and regulations to ensure compliance, such as those set by ERISA or the ACA.
- Administrative Burden: Managing the plan’s compliance, claims processing, and other tasks can require additional time and expertise, leading to higher administrative costs.
Self-Insured Health Plans vs. Fully Insured Health Plans
Choosing the right health insurance is a critical decision for individuals and employers alike. Health plans generally fall into two categories: self-insured and fully insured. Each option works differently in terms of cost responsibility, flexibility, and risk management. Understanding these differences helps you make an informed choice based on your healthcare needs and financial goals.
| Criteria | Self-Insured Health Plans | Fully Insured Health Plans |
| Cost | Lower premiums, no insurer profit margin. | Higher premiums to cover insurer’s risk and profit. |
| Flexibility in Coverage | Customizable; coverage is based on needs. | Limited customization; coverage predefined by the insurer. |
| Risk Management | The individual or employer assumes financial risk. | The insurer assumes the financial risk of medical costs. |
| Administrative Burden | Managed by the individual or a TPA. | Insurance company handles all administration. |
Before choosing between a self-insured and a fully insured health plan, it’s important to understand how these two options differ in cost, flexibility, risk, and administration. While both plans provide health coverage, they operate in very different ways and suit different types of individuals and businesses. The comparison below highlights the key differences to help you decide which option aligns better with your healthcare needs, financial capacity, and long-term planning goals.
Who Should Consider Self-Insured Health Plans?

Self-insured health plans are not suitable for everyone. However, they may be a good option for:
1. Self-Employed Individuals
For the self-employed, a self-insured health plan can offer more control over healthcare costs, especially when linked to an HSA. This flexibility can also come with tax benefits, making it an attractive option.
2. Small to Medium-Sized Businesses
Small businesses often face high premiums for traditional health insurance. Self-insurance offers the potential for savings by eliminating insurer profit margins and allows businesses to customize the plan to meet employees’ needs.
3. Large Employers
Larger businesses with a stable workforce and predictable healthcare needs may find self-insurance beneficial. It offers significant cost savings and flexibility in designing employee benefits but requires substantial financial reserves to cover larger claims.
4. Individuals with Predictable Healthcare Needs
Those with stable, predictable healthcare needs such as individuals with chronic conditions may benefit from self-insured plans, as they can manage expenses more effectively.
Key Considerations Before Choosing a Self-Insured Health Plan
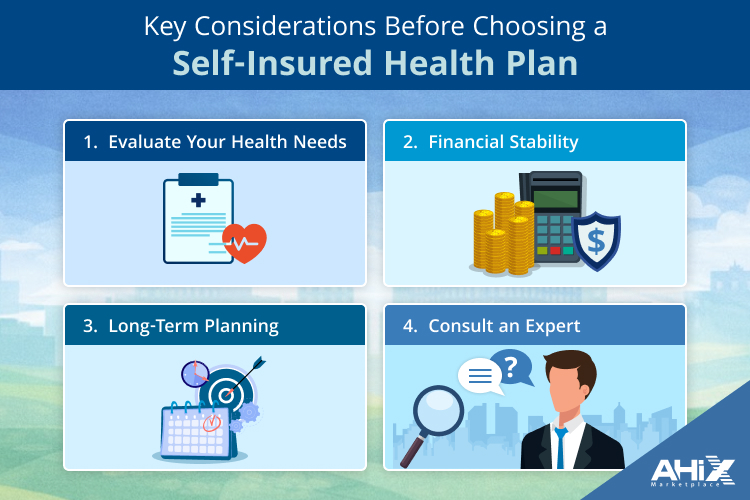
Before opting for a self-insured health plan, here are key factors to consider:
1. Evaluate Your Health Needs
If you or your employees have predictable healthcare needs, a self-insured plan may be a good fit. However, for those with unpredictable health conditions, the financial risk can be significant.
2. Financial Stability
Self-insured plans require upfront funding. Ensure that you have the financial reserves or capital to manage the potential costs.
3. Long-Term Planning
Self-insured plans require careful long-term planning to account for unpredictable medical expenses. It’s crucial to set aside funds in an HSA or similar account for unexpected events.
4. Consult an Expert
Before deciding on a self-insured health plan, it’s wise to consult with a financial advisor or insurance expert. They can help you assess the feasibility and guide you on best practices for managing the plan.
Conclusion
Self-insured health plans offer a unique alternative to traditional health insurance, providing individuals and businesses with more control over their healthcare costs. They can offer substantial savings, customization, and flexibility but come with risks such as high upfront costs and the unpredictability of medical expenses.
If you have predictable healthcare needs or sufficient financial stability, self-insured plans could be a cost-effective solution. Small businesses and self-employed individuals may find them particularly advantageous, while larger employers can benefit from the flexibility in plan design and potential savings.
Before opting for a self-insured plan, it’s important to carefully consider your healthcare needs, evaluate your financial resources, and consult with an expert to ensure it’s the right fit.
FAQs
1. What are the main differences between a self-insured health plan and a fully insured health plan?
A self-insured health plan allows individuals or employers to assume financial responsibility, while fully insured plans transfer the risk to an insurance company. Self-insured plans offer lower costs and more flexibility but come with higher risk.
2. Can self-insured health plans be used for small businesses?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from self-insured plans by reducing healthcare costs. These plans offer flexibility and customization, but they require significant upfront funding and careful financial planning.
3. How does stop-loss insurance work with self-insured health plans?
Stop-loss insurance provides protection by covering large medical claims that exceed a certain threshold, helping prevent catastrophic financial loss for the individual or employer.
4. What are the tax advantages of self-insured health plans?
Self-insured plans linked to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) offer tax-free contributions, tax-deferred growth, and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses.
5. Is a self-insured health plan a good option for people with chronic health conditions?
Self-insured plans can be ideal for individuals with chronic health conditions if their healthcare needs are predictable. However, it’s important to assess the potential for major medical expenses and the need for stop-loss insurance.



